Neutron Star
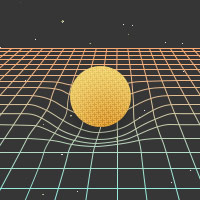
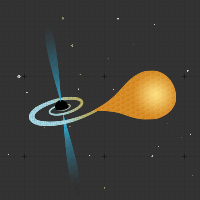
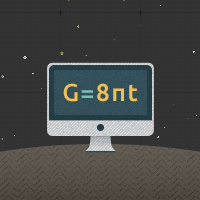
A type of star which is very old, having cooled off and stopped nuclear fusion reactions. When gravity pulls the star down on itself, the electrons and protons are squeezed together, leaving just neutrons. The star is then supported against gravity by "neutron degeneracy pressure" (no two neutrons can be in the same place at the same time). These are produced when a star is too heavy to be a white dwarf, but not heavy enough to turn into a Black Hole.