B
B
Big Bang
An astrophysical theory of the beginning of the Universe. It suggests that the Universe began in a very tiny region of space, and exploded outward. Astrophysicists believe that this occurred roughly 14 billion years ago. Other astrophysical theories for the beginning of the Universe — like the Braneworld theory — exist, though none is as thoroughly studied and supported by the data as the Big Bang model. Scientists have no idea what came before the Big Bang.
Big Crunch
Essentially the opposite of the Big Bang, the Big Crunch is one possible fate of the Universe. If the matter and energy of the Universe are not moving outward quickly enough, gravity could pull the Universe in on itself, collapsing it in a final Big Crunch. It is not yet known whether this will happen to our Universe.
Black Hole
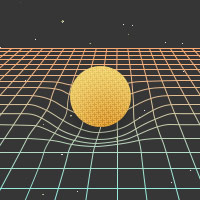
A region of spacetime where the warpage of both space and time (gravity) is so intense that nothing — even light — can ever escape. Objects may fall in to the Black Hole, but once they pass the Event Horizon, they can never escape again. Most Black Holes believed to exist are thought to be formed in the collapse of very large stars, or the collision of stars or other Black Holes.
Boson
A type of particle with "integral angular momentum" — a spin of 0, 1, 2, etc. Spin refers to an intrinsic quality of all particles. Examples of fermions are photons (which are the particles which give us light) and gravitons (which give us gravity). The other type of particle is the fermion.
Boundary
A division between two regions. Physicists frequently analyze only a part of a larger system, so that they do not need to keep track of everything. This usually simplifies the analysis, but requires an understanding of what happens at the boundary. Interesting computer simulations usually require a boundary.
Boundary Conditions
The state of a physical system at a boundary. Interesting computer simulations usually require boundary conditions.
Brane
Objects which arise in string theory. They can have any number of dimensions, and are usually imagined as existing in a space with more dimensions than the brane itself has.
Braneworld
A four-dimensional surface — a "brane" — in a spacetime with more than four dimensions.